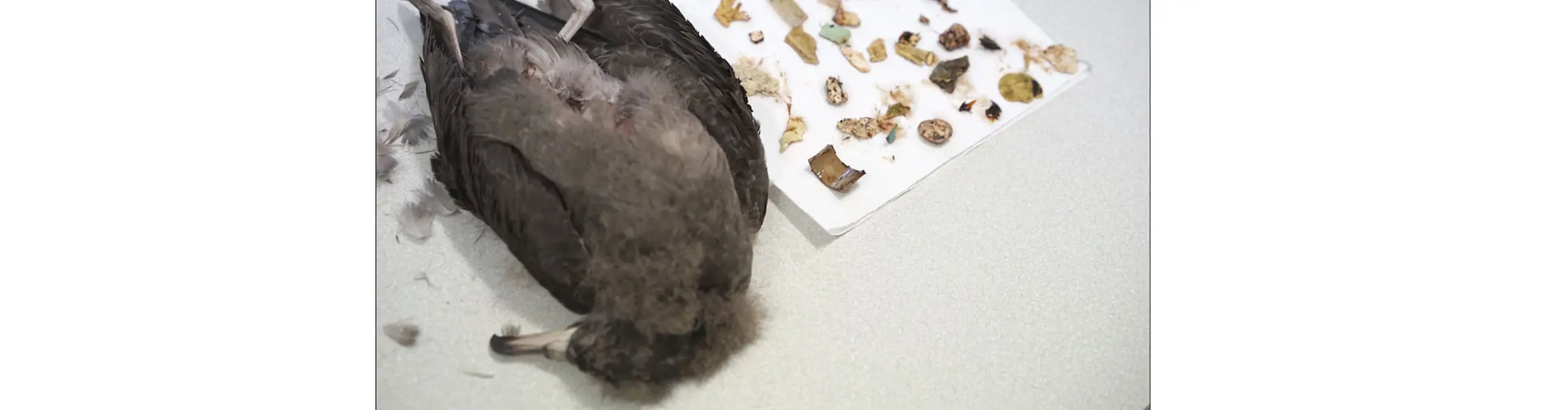
De vogels kunnen er ogenschijnlijk gezond uitzien, maar toch verzwakt zijn. De inwendige littekens in magen werden geconstateerd bij vrijwel alle dertig onderzochte vogels. Het artikel verscheen in het Journal of Hazardous Materials.
Stormvogels leven volledig op zee, behalve tijdens het broedseizoen. Voor hun voedselvoorziening duiken ze metersdiep onder water om hun prooi te vangen, of ze plukken het voedsel op van net onder het wateroppervlak.
Broedkolonie op Lord Howe
Op het Lord Howe-eiland, oostelijk van Australië, wordt al jaren onderzoek gedaan naar de Australische grote pijlstormvogel (Ardenna carneipes). Deze soort, die daar broedt, krijgt veel plastic binnen krijgt. De onderzoekers vonden niet alleen plastic deeltjes terug in de magen, maar zagen ook littekens in maagwanden die veroorzaakt zijn door ingeslikt plastic. Omdat zoveel vogels deze door plastic veroorzaakte wonden hadden, hebben ze de ziekte een naam gegeven: plasticose.
Stapeling van schadelijke gevolgen
Het binnenkrijgen van plastic heeft allerlei gevolgen voor deze zeevogel. Ingeslikt plastic kan zorgen voor verstoppingen in het verteringsstelsel en ondervoeding. Plastics kunnen daarnaast ook giftige chemicaliën afgeven. Veel van deze chemicaliën hebben een hormoonverstorende werking en kunnen via de moeder in haar eieren terechtkomen. Dat kan leiden tot levenslange gevolgen voor de vogels. Er zijn ook relaties aangetoond tussen de hoeveelheid plastic en bloedwaarden van jonge stormvogels.
Sommige stukken plastic hebben scherpe kanten of zijn uitzonderlijk groot. Dat ingeslikt plastic ook interne wonden maakt, is een nieuw gegeven.
In elke bolus werd plastic aangetroffen
De pijlstormvogel neemt voedsel van zee mee voor de kuikens. Die braken na enige tijd een bolus uit. De groep onderzocht tussen 2002 en 2020 ook bolussen op Lord Howe. In alle bolussen werd plastic aangetroffen, met een gemiddelde van 21,8 stukjes plastic. Ook is onlangs door dezelfde onderzoeksgroep vastgesteld dat het gemiddeld gewicht van de kuikens tussen 2010 en 2022 afnam, waardoor de kans toeneemt dat kuikens na het uitvliegen sterven.
Met de stapeling van schadelijke effecten, vrezen de onderzoekers op termijn voor het voortbestaan van deze soort.
Foto: Cameron Muir